Evaluate LLM Applications with Ragas Metrics in Opik
The Opik SDK provides a simple way to integrate with Ragas, a framework for evaluating RAG systems.
There are two main ways to use Ragas with Opik:
- Using Ragas to score traces or spans.
- Using Ragas to evaluate a RAG pipeline.
Account Setup
Comet provides a hosted version of the Opik platform, simply create an account and grab your API Key.
You can also run the Opik platform locally, see the installation guide for more information.
Getting Started
Installation
You will first need to install the opik and ragas packages:
Configuring Opik
Configure the Opik Python SDK for your deployment type. See the Python SDK Configuration guide for detailed instructions on:
- CLI configuration:
opik configure - Code configuration:
opik.configure() - Self-hosted vs Cloud vs Enterprise setup
- Configuration files and environment variables
Configuring Ragas
In order to use Ragas, you will need to configure your LLM provider API keys. For this example, we’ll use OpenAI. You can find or create your API keys in these pages:
You can set them as environment variables:
Or set them programmatically:
Using Ragas to score traces or spans
Ragas provides a set of metrics that can be used to evaluate the quality of a RAG pipeline, a full list of the supported metrics can be found in the Ragas documentation.
You can use the RagasMetricWrapper to easily integrate Ragas metrics with Opik tracking:
Once the metric wrapper is set up, you can use it to score traces or spans:
In the Opik UI, you will be able to see the full trace including the score calculation:
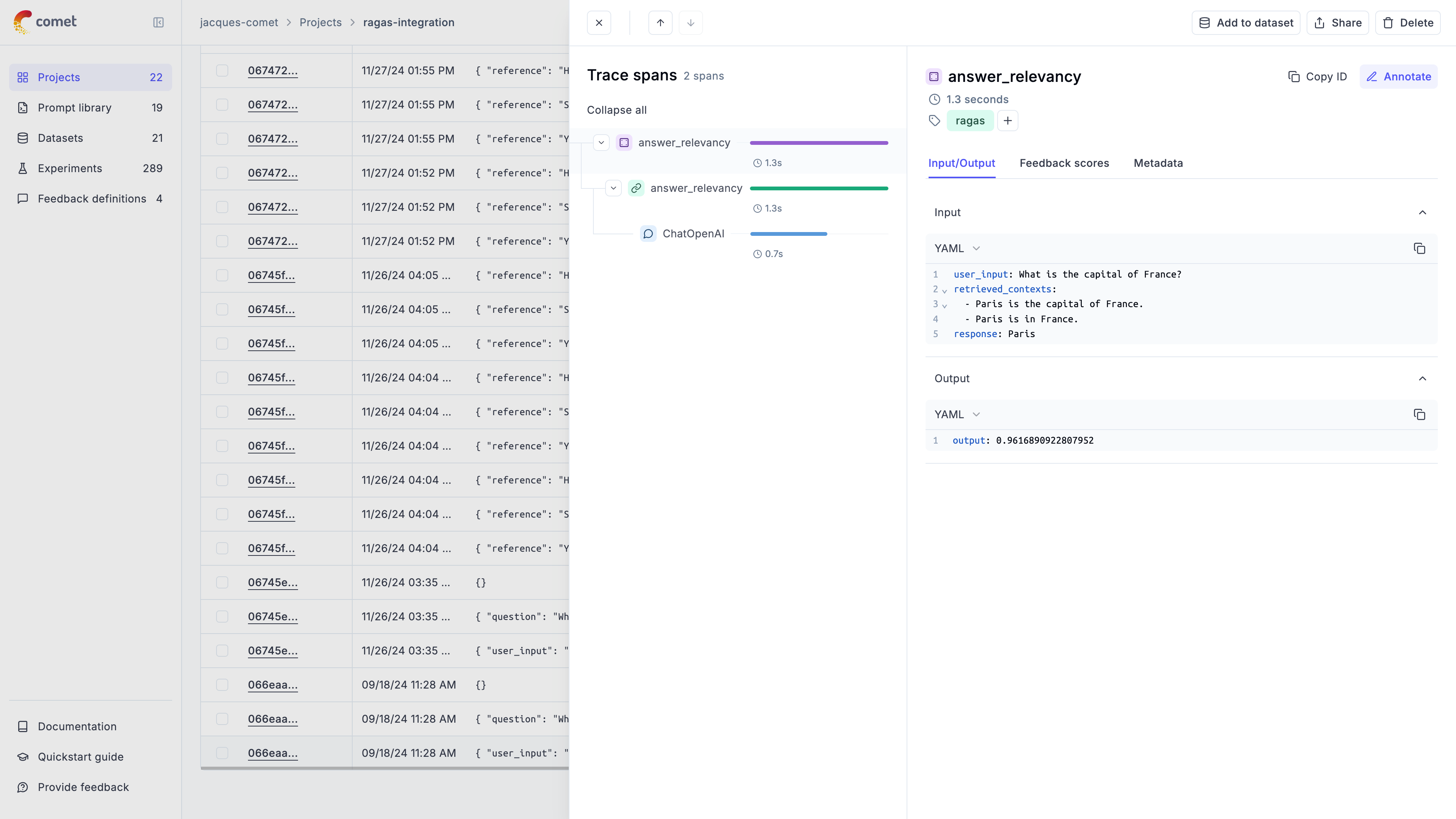
Comprehensive Example: Dataset Evaluation
For more advanced use cases, you can evaluate entire datasets using Ragas metrics with the Opik evaluation platform:
1. Create a Dataset
2. Define Evaluation Task
3. Run Evaluation
4. Alternative: Using Ragas Native Evaluation
You can also use Ragas’ native evaluation function with Opik tracing:
Using Ragas metrics to evaluate a RAG pipeline
The RagasMetricWrapper can also be used directly within the Opik evaluation platform. This approach is much simpler than creating custom wrappers:
1. Define the Ragas metric
We will start by defining the Ragas metric, in this example we will use AnswerRelevancy:
2. Create the metric wrapper
Simply wrap the Ragas metric with RagasMetricWrapper:
If you are running within a Jupyter notebook, you will need to add the following line to the top of your notebook:
3. Use the metric wrapper within the Opik evaluation platform
You can now use the metric wrapper directly within the Opik evaluation platform:
The RagasMetricWrapper automatically handles:
- Field mapping between Opik and Ragas (e.g.,
input→user_input,output→response) - Async execution of Ragas metrics
- Integration with Opik’s tracing system when
track=True - Proper error handling for missing required fields

