Introduction
Google has taken a significant leap by introducing the Gemini AI, its latest large language model (LLM), to the public. This milestone will bring widespread changes across all of Google’s products. With the capability to perform tasks more akin to human actions, Gemini represents a crucial stride toward achieving artificial general intelligence (AGI).
What is Gemini?
Google introduced Gemini, an innovative artificial intelligence (AI) system capable of intelligently comprehending and conversing about various prompts, including pictures, text, speech, music, computer code, and more. This form of AI is called a multimodal model, representing a significant advancement beyond the capability to handle only text or images.
Gemini is more than just a single AI model, and one notable feature of Gemini is its capacity for visual language interpretation. It was released on 06 December 2023.
Different Versions of Gemini
Gemini is a flexible model that works well on various platforms, including data centers and mobile devices. As a result, it has been made available in three different versions.
- Gemini Nano: Crafted for mobile devices, especially the Google Pixel 8, Gemini Nano excels in compact on-device AI processing. This lightweight model ensures efficient offline performance, delivering powerful AI capabilities for tasks like suggesting chat replies and text summarization on smartphones.
- Gemini Pro: The advanced variant fuels Google’s latest AI chatbot, Bard, ensuring swift responses and adept query handling. Integrated into data centers, Gemini Pro enhances Bard’s reasoning, planning, and understanding capabilities, marking a significant stride in efficient AI-driven interactions.
- Gemini Ultra: Google asserts it is the most advanced model, surpassing state-of-the-art results and widely-used academic benchmarks in large language model (LLM) research and development. They are specifically designed to tackle highly complex tasks.
Gemini’s Training
The training of Gemini, Google’s powerful multimodal AI model, involved several vital aspects:
Data:
- Massive and diverse: Gemini was trained on a vast dataset of text, code, images, audio, and other modalities. This diversity helps it understand different types of information and make connections between them.
- High-quality: The data was carefully curated and filtered to ensure accuracy and relevance. This helps prevent biases and promotes reliable performance.
Training Techniques:
- Multimodal learning: Gemini leverages multimodal learning, which simultaneously processes information from various modalities. This allows it to understand the relationships between different data types, leading to a richer understanding of the world.
- Transfer learning: The model also benefits from transfer learning, where knowledge gained from pre-trained models on specific tasks is transferred to new tasks. This helps it learn faster and achieve better performance.
Hardware:
- Custom TPUs: Google employed their specially designed Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) v4 and v5e. These advanced AI accelerators allowed for efficient and scalable training, handling the immense processing demands of the model.
Architecture
The researchers did not disclose the full architecture details. Still, they mentioned that Gemini models are constructed upon a transformer decoder architecture similar to the one used in popular NLP models like GPT-3. However, not all specifics of the architecture were revealed. The models are written in Jax and trained using TPUs.
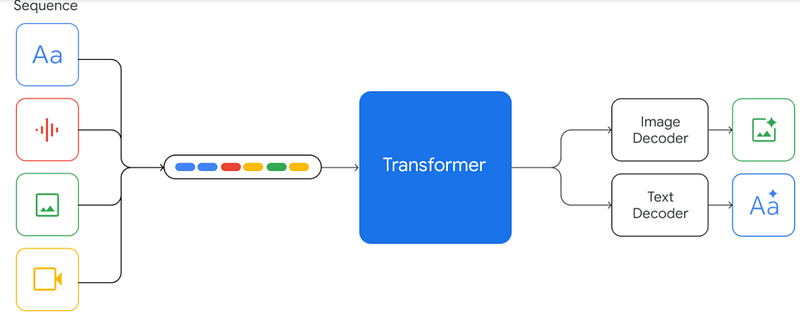
Input sequence: The user enters data in various formats, including text, graphs, photos, audio, video, and 3D models.
Encoder: These inputs are taken by the encoder, transforming them into a language the decoder can comprehend. The various data types are transformed into a single, cohesive representation to achieve this.
Model: The model is fed the encoded inputs. No information about the task’s specifics is required of the multimodal model. It only handles the inputs by the current job.
Image and text decoder: The decoder creates the outputs by processing the model’s inputs. Gemini can only produce text and image outputs at this time.
Features of Gemini
The Google Gemini models excel in various tasks spanning text, image, audio, and video understanding. These features offer insights into how Gemini outperforms other AI systems.
- Multimodal capabilities: It increases its capacity to understand and produce content in various modes. Because of its adaptability, Gemini can process text, comprehend fine details from images, and identify patterns in audio. It can also interpret and navigate a variety of information sources with ease.
- Problem-solving and reasoning: Gemini has strong analytical and problem-solving skills comparable to human cognitive processes. It can handle complex tasks like evaluating academic work or analyzing large, complex data sets—an efficient way to assess numerous workpieces simultaneously.
- Advanced coding: Programming languages that are most widely used worldwide, including Python, Java, C++, and Go, can be understood and explained, and high-quality code can be generated using the first version of Gemini. As one of the top foundation models for coding worldwide, it can reason about complex information and operate across multiple languages.
- Multiple Versions: Three versions are available for the model: Pro, Nano, and Ultra, which is the most advanced. Every version meets different needs and degrees of complexity.
Accessing Gemini
Feel free to explore Google’s new AI technology once you’re familiar with it. No waiting period or beta testing is necessary; Gemini Pro is available through the Bard chatbot website. Accessing Gemini Pro depends on how you want to use it:
Through Google AI Platform:
- Sign up for Google AI Platform (AIP): If you haven’t already, create an account on AIP. You can get started for free with a trial access.
- Enable the Gemini Pro API: Head to the “Marketplace” section in AIP and search for “Gemini Pro.” Click on it and enable the API.
- Use the API or Notebook: You can access Gemini Pro through either the API directly or via a pre-built Jupyter Notebook provided by Google. The notebook offers a user-friendly interface for experimenting with the model.
Through Python:
- Install the necessary libraries: You’ll need the
google-cloud-aiplatformlibrary and any other libraries specific to your chosen use case. - Authenticate with AIP: Use your AIP credentials to authenticate with the platform through the library.
- Create a Predictor object: This object allows you to send requests to the Gemini Pro model and receive responses.
- Send your prompt and interpret the result: Craft your query or task for Gemini Pro and send it through the Predictor object. The model will return its response, which you can then analyze and use.
How does Gemini differ from other AI models, like GPT-4?
Architecture
GPT-4 has an unimodal architecture that only pays attention to text—crafted for diverse textual uses, providing adaptability in managing Natural Language Processing (NLP). Gemini has a Multimodal architecture that integrates text and images, enabling more dynamic interactions and a greater variety of NLP applications.
Learning Capability
GPT-4 allows for incremental learning through version updates, but Gemini has constant learning based on real-time data, which could result in quick updates to our knowledge.
Data Training
GPT-4’s training on an extensive dataset until a specific cut-off date limited its understanding of recent events. Meanwhile, Gemini is trained on real-time data, allowing for up-to-date responses and insights.
Techniques
GPT-4 uses deep learning for text processing, which works well for various language tasks. However, Gemini uses methods for problem-solving inspired by AlphaGo, enabling sophisticated planning and reasoning in challenging tasks.
Application Scope
GPT-4 is mainly employed for text-based programs, customer support, content production, and instructional settings. However, Gemini is anticipated for a broader range of applications, such as image processing, complicated problem solving, and dynamic content creation.
Future of Gemini
The future of Gemini depends on how we develop and deploy it. Google will likely continue to invest in Gemini’s development, improving its accuracy, expanding its knowledge base, and adding new capabilities. This could include:
- Handling even more modalities: Integrating new data types like video, sensor data, and virtual reality experiences.
- Understanding more complex tasks: Moving beyond text generation and code editing to function reasoning, planning, and decision-making tasks.
It’s important to remember that AI is still developing, and predicting its long-term impact is complex. However, by staying informed and engaging in constructive conversations about the future of AI, we can ensure that it benefits all of humanity.
Conclusion
The landscape of AI shifts with Gemini’s arrival. Its inherent flexibility, stemming from its mastery of multiple data modalities, positions it as a universal tool capable of tackling an unprecedented range of tasks. Witnessing its future development and applications promises to be a fascinating journey.