“SSL:CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED” Error in Comet— Fixed

The funny thing about programming is that bugs can often be a real headache. For example, a code running today may be broken tomorrow if poorly managed by the developers. Whenever a bug is found, the debugging process has to take place in order to solve the issue at hand.
Recently I was working with Comet, and I was trying to log my visualizations to the platform after I have created my account, copied my API keys, and also written my code in my Jupyter notebook.
I was getting the “SSL:CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED” error repeatedly anytime I try to deploy my code to the platform.
Here is what the error looks like:

If you are experiencing this, then let us walk through the issue together and solve this error.
Comet
Comet is an experimentation platform that allows you to track, monitor, and compare your Machine Learning experiments. You can write your code in your preferred language, and then compare the results of your experiments in the Comet interface. I personally use Comet with python, but you can also use Comet with R and Java.
Let’s have a look at the code I wrote.
# importing the required libarary
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df = pd.read_excel("online_retail_II.xlsx")
df.head()
#Bar chart visualisation
mask_df = df["Country"].value_counts().head(10)
fig1 = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.bar(x = mask_df.index, height=mask_df, color="sienna")
plt.xlabel("Country")
plt.ylabel("Counts")
plt.title("Numbers of Orders from Countries Over the Years")
plt.xticks(rotation=45);
#Histogram visualization
fig2 = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
sns.histplot(df["InvoiceDate"], color="darkslategrey", bins=50)
plt.title("Distribution of the Invoice Date");
# import comet_ml at the top of your file
from comet_ml import Experiment
# Create an experiment with your api key
experiment = Experiment(
api_key = "your API key",
project_name = "viz",
workspace="zenunicorn",
)
#logging the viz to comet
experiment.log_figure(figure_name="Matplotlib Viz", figure=fig1)
experiment.log_figure(figure_name= "Seaborn Viz", figure=fig2)
#always end your experiment
experiment.end()
@zenUnicorn
From the code above,
- We imported the necessary libraries needed to perform this experiment, such as pandas, seaborn, and matplotlib.
- In the next two code segments, we visualized the dataset using a bar chart and a histogram.
- Finally, we imported Comet into our project and logged the visualizations to the Comet platform.
It is at this stage that you will notice the error popping up everywhere on your screen.
Note: It is important that you have a stable internet connection when deploying to Comet, in order to avoid running into errors.
Fixing the error
Often time the people that run into these errors are users on macOS or OSX, and this is because python 3.6 or higher has no certificates installed at all, therefore it can’t validate any SSL connections. This means we will get errors whenever we try to connect to an HTTPS:// website.
This is a change in new versions of python 3 and requires a post-install step, in which we have to install the certifi package of certificates. We can check out the documentation which is available in the ReadME.rtf file in our python applications directory, accessible via: /Applications/Python/3.9/ReadeMe.rtf .
Let’s copy and paste this code into our IDE (I am using Jupyter notebook).
# install_certifi.py
#
# sample script to install or update a set of default Root Certificates
# for the ssl module. Uses the certificates provided by the certifi package:
# https://pypi.python.org/pypi/certifi
import os
import os.path
import ssl
import stat
import subprocess
import sys
STAT_0o775 = ( stat.S_IRUSR | stat.S_IWUSR | stat.S_IXUSR
| stat.S_IRGRP | stat.S_IWGRP | stat.S_IXGRP
| stat.S_IROTH | stat.S_IXOTH )
def main():
openssl_dir, openssl_cafile = os.path.split(
ssl.get_default_verify_paths().openssl_cafile)
print(" -- pip install --upgrade certifi")
subprocess.check_call([sys.executable,
"-E", "-s", "-m", "pip", "install", "--upgrade", "certifi"])
import certifi
# change working directory to the default SSL directory
os.chdir(openssl_dir)
relpath_to_certifi_cafile = os.path.relpath(certifi.where())
print(" -- removing any existing file or link")
try:
os.remove(openssl_cafile)
except FileNotFoundError:
pass
print(" -- creating symlink to certifi certificate bundle")
os.symlink(relpath_to_certifi_cafile, openssl_cafile)
print(" -- setting permissions")
os.chmod(openssl_cafile, STAT_0o775)
print(" -- update complete")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()

- The code runs and first installs the
certifipython package. - It also creates a symbolic link from the OpenSSL certificates file to the certificates file installed by the package
certifi.
The Certificates.command file is installed into our python app directory, it is basically a terminal script so we just click on it and allow it to run. Close it after it is done running.
We have to head back to our terminal and restart the Jupyter notebook. After that is done we can now try to deploy to Comet agai346806n, we will notice that it works perfectly without the SSL Certificate Errors, and all our visualizations are logged into our project.
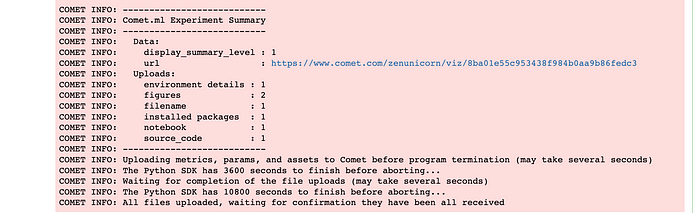
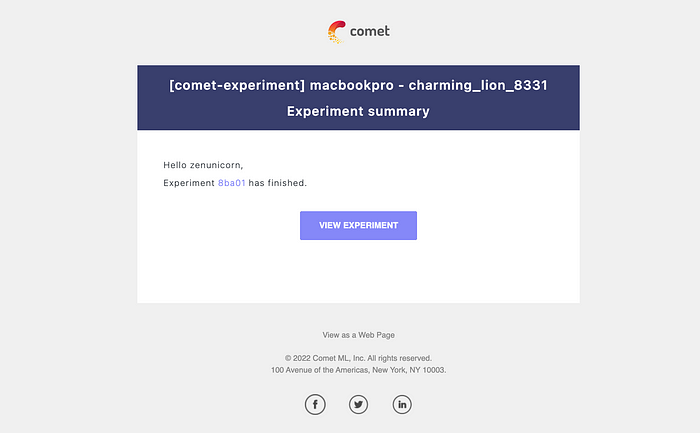
We will also get an email notification that our experiment has been logged.
Conclusion
We have successfully solved the SSL error and it is working perfectly now, although windows OS users are not likely to have this type of error unlike OSX users, if a windows OS user runs into the same issues this method is the best approach to solving it.
Bid farewell to emailing Jupyter notebook by signing up on Comet today.